Mit App Inventor 2 Get Travel Speed
The LocationSensor component is a simple control that is difficult to use without knowledge of some basic concepts of geo-location. The LocationSensor is used to communicate with the global positioning satellite receiver (GPS) in your phone/tablet. When the LocationSensor communicates with the built-in GPS receiver, the GPS determines the location of your device. The sensor tin can also work with network/wifi location services. Finding a location through the network uses very different techniques than with a GPS. Location means the device'south present latitude and longitude, or it can hateful your street address. The measuring units employed in the LocationSensor for altitude are meters. Time is measured in milliseconds (ms). Be enlightened that one second = 1000 ms. and 60000 ms is i minute.
When the sensor reports distance information or y'all gear up a distance into the component, the units are in meters. If your app must deal in English units, use the Math blocks to catechumen units at the time you display them. Calculate everything in meters, then convert to report the event in anxiety or miles on your display. Think meters!
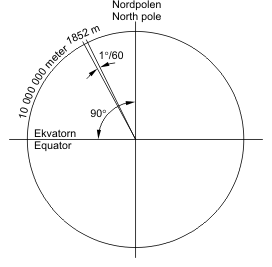 A nautical mile is the distance subtended by a minute of angle (1/60 of a degree) across the earth's radius. This means that the distance between a degree of latitude and the adjacent whole caste is sixty nautical miles. A degree of longitude is lx nautical miles at the equator, but the separation betwixt next whole degrees of longitude diminishes as y'all alter latitude toward the poles. The spacings between degrees of breadth are constant; the spacing between degrees of longitude are variable.
A nautical mile is the distance subtended by a minute of angle (1/60 of a degree) across the earth's radius. This means that the distance between a degree of latitude and the adjacent whole caste is sixty nautical miles. A degree of longitude is lx nautical miles at the equator, but the separation betwixt next whole degrees of longitude diminishes as y'all alter latitude toward the poles. The spacings between degrees of breadth are constant; the spacing between degrees of longitude are variable.
Electric current app developers think in terms of meters, but a long time ago, navigators described their ship'south position with respect to the English language units of degrees, minutes and seconds. Latitude and longitude are withal described in terms of degrees, minutes and seconds. These are awkward units for utilise on a figurer, so developers and others normally use decimal latitude and longitude descriptions, to brand the math calculations easier. Looking at 0.00001 of a caste of latitude, it converts to 0.9144 meters. Therefore, satellite positional information is precise to 0.ix meters. The best accurateness possible with specialized GPS receivers is approximately three meters. In that location are techniques to make the resolution better. As you develop apps with this tool, exist enlightened the GPS in your device can practice a lot, simply its accuracy is limited in many situations.
Y'all will practice your best job of developing apps using the LocationSensor if y'all understand how a GPS system works. Geo-location principals are described near the end of the tutorial.
GPS Accurateness Logger A Unproblematic GPS App
GPS Accuracy Logger is an app that demonstrates the utilize of a device'south Global Positioning Satellite (GPS) receiver. The app also demonstrates how the accuracy of a device's GPS varies depending on where the device is located. The LocationSensor component instructs the GPS receiver in the mobile device to get a satellite set (discover a satellite, determine that the information from the satellite is valid, notice at to the lowest degree two more satellites to confirm the information, and simply then written report the data back to your device). Some GPSes tin utilize from between 12 and 20 satellites to become a very authentic fix, providing the GPS receiver is capable of receiving 12 or 20 channels of data. Many simple devices will simply utilize a few satellites.
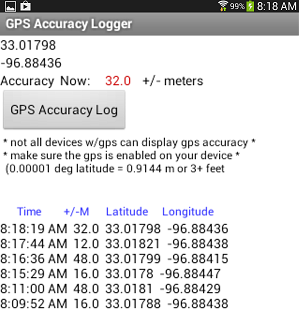
The logger app captures breadth/longitude positional data and provides a numerical estimate of the reliability of the GPS' satellite fix (Accuracy). Pocket-size accuracy values indicate better accurateness. The app reports what the GPS resolves as latitude and longitude and demonstrates how the device accuracy might vary as the GPS updates its satellite fixes, or every bit the device is moved from outside to inside a building or loses a set on the satellites information technology uses to determine location.
Note in the paradigm below the modify in the accuracy readings captured over a short menstruum of fourth dimension (8 minutes). This device was stationary on a desk-bound inside a building when it captured the readings and there is pregnant variation in the ability of the device to provide authentic location data. Satellites continually motion around the Earth. The GPS in the device loses accuracy as the number of satellites it can receive decreases. The accurateness normally increases as the GPS receives more than satellites. MIT App Inventor tin study the accuracy of any fix provided the GPS receiver on the device has the capability of reporting accuracy (i of the many backdrop of the LocationSensor described afterward). The GPS is designed to use every bit much information and from every bit many satellites equally possible to provide the best possible accuracy at whatsoever instant in time. Below is a give-and-take of why accuracy matters, what causes it to fluctuate and what a developer can do to minimize the impact on the users of the app by avoiding the reporting of 'suspicious' location data.
Note: To exam this app, you lot must use a device with GPS capabilities. Testing with an emulator will not give you true location information. Beneath is a short discussion of what can be done to provide location data by connecting to a network or through WIFI. Phones/tablets without a GPS receiver tin provide location data (although it is less precise).
Satellites transmit information using NMEA 0183 format, a standard for communicating with marine electronic devices, also used for GPSes. The NMEA data stream is a compilation of lots of data transmitted from a satellite in text format. MIT App Inventor cannot interpret all the data available in the data stream circulate from the satellites. Despite the limitations of the LocationSensor component, AI2 provides the bones functionality needed to get location information from your device.
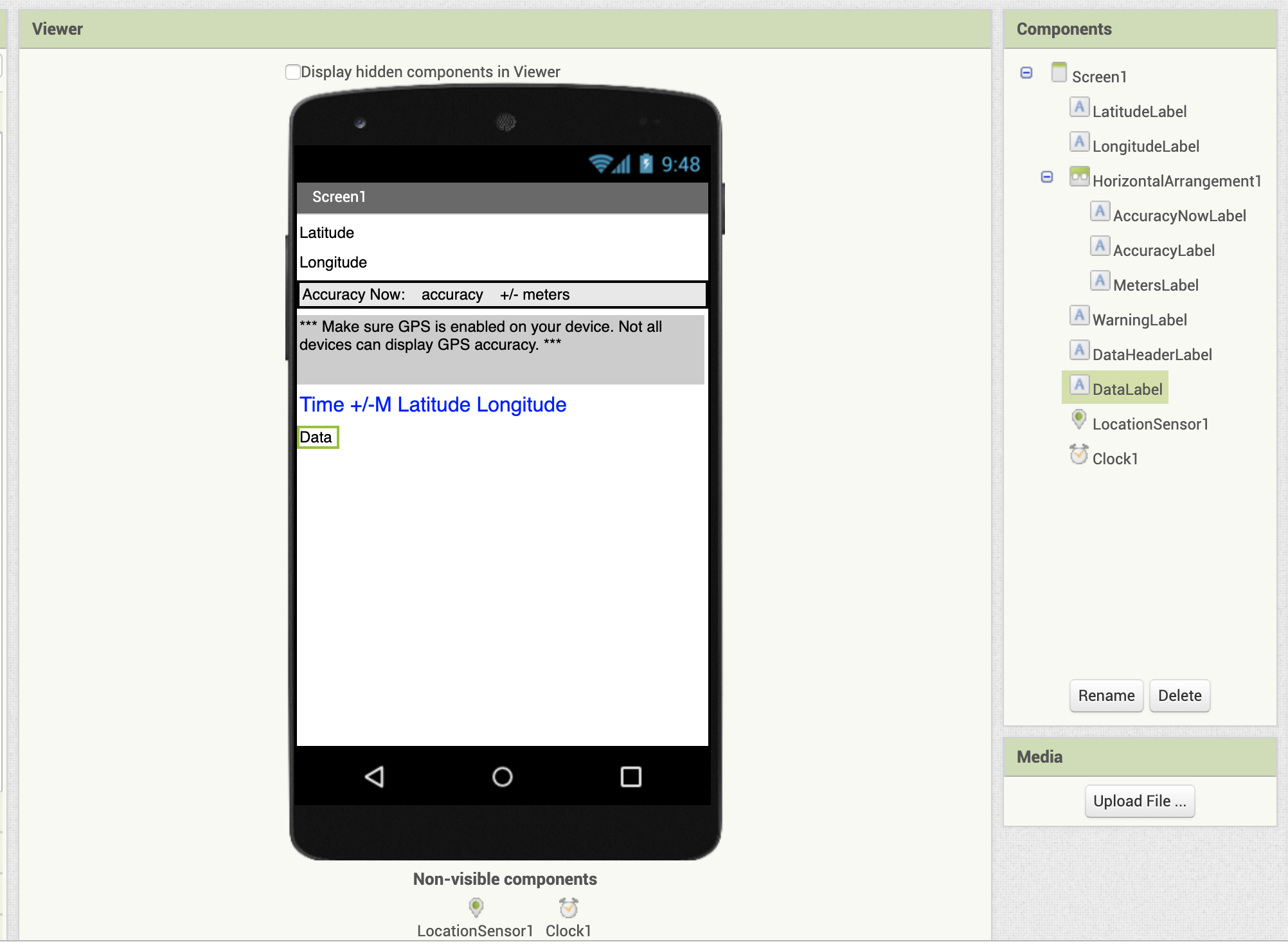
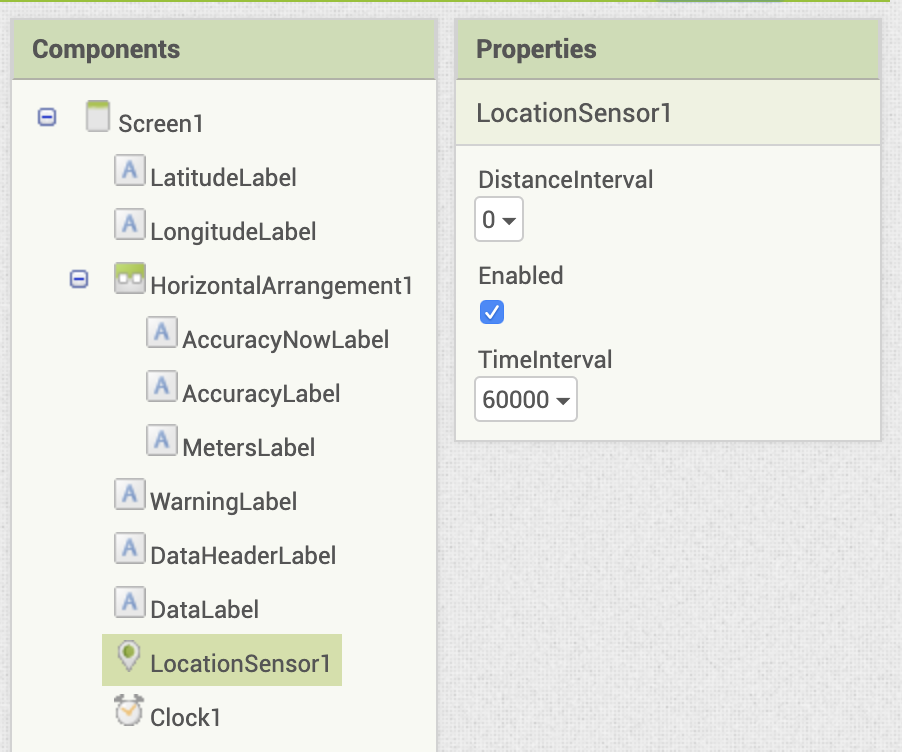
The GPS Accuracy Logger app requires just a few components and blocks. In the Designer, add the following components, and prepare the properties as listed.
| Component | Component Drawer | Component Name | Purpose | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | User Interface | LatitudeLabel | Displays the current latitude reading from the LocationSensor | Text: Latitude |
| Label | User Interface | LongitudeLabel | Displays the current longitude reading from the LocationSensor | Text: Longitude |
| HorizontalArrangement | Layout | HorizontalArrangement1 | Holds the next 3 Labels so they announced side by side to each other | Width: Fill up Parent |
| Label | User Interface | AccuracyNowLabel | Displays characterization for presenting current accuracy | Text: Accuracy Now: |
| Characterization | User Interface | AccuracyLabel | Displays the current accuracy value from the LocationSensor | Text: accuracy |
| Label | User Interface | MetersLabel | Displays the label for +/- meters post-accurateness label | Text: +/- meters |
| Label | User Interface | WarningLabel | Notifies user of information virtually GPS accuracy on devices | Width: 98% BackgroundColor: LightGray Text: *** Make sure GPS is enabled on your device. Non all devices can brandish GPS accuracy. *** |
| Characterization | User Interface | DataHeaderLabel | Display heading for accurateness data | Text:" Time +/-M Latitude Longitude" TextColor: Blueish |
| Label | User Interface | DataLabel | Display information received from LocationSensor | Text: "" (blank) |
| LocationSensor | Sensors | LocationSensor1 | Provides location information from GPS inside device | DistanceInterval: 0 TimeInterval: 60000 |
| Clock | Sensors | Clock1 | Will be used to poll the LocationSensor periodically for accuracy data. | TimerInterval1000 |
Your Designer Viewer and Component list should look similar to this:
Switch to the Blocks Editor. Initialize a variable LS_Accuracy to 1. This will hold the accuracy value nosotros receive from the LocationSensor. 
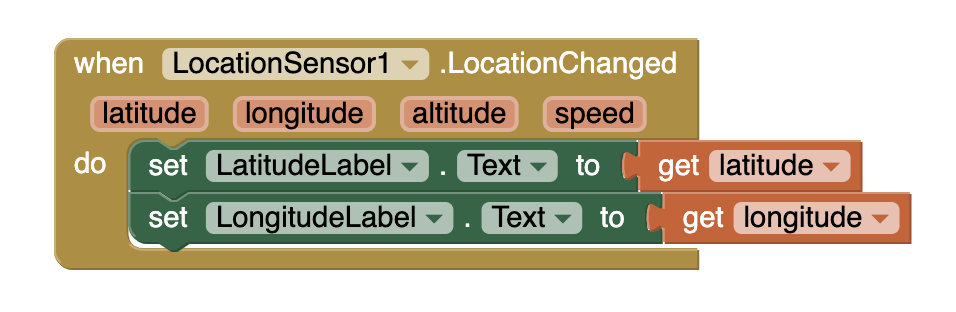
The LocationSensor1.LocationChanged event block is triggered when the GPS confirms a location modify on the device. The latitude and longitude reported are in decimal degrees. Set up the reported latitude and longitude in the appropriate labels in the app.
The Clock1.Timer volition trigger every 2d and cheque the accuracy of the LocationSensor. The if-else block tests to run across if the accuracy is less than or equal to 10 meters and changes the text color for the AccuracyLabel to either black (<= 10 meters) or ruddy (> ten meters).
The 2nd if-and then cake compares the current accuracy value with the accuracy determined during a previous check and stored in the LS_Accuracy variable. If the accuracy has inverse, the app reports a new line in the data list. The list enumerates the latest accuracy, latitude and longitude. This "list" is displayed at the lesser of the app's screen. The \north symbol is used to forcefulness each data set (consisting of time, accuracy, latitude, longitude) onto individual lines.
And finally, the accurateness is saved to the variable LS_Accuracy for comparison on the next iteration.
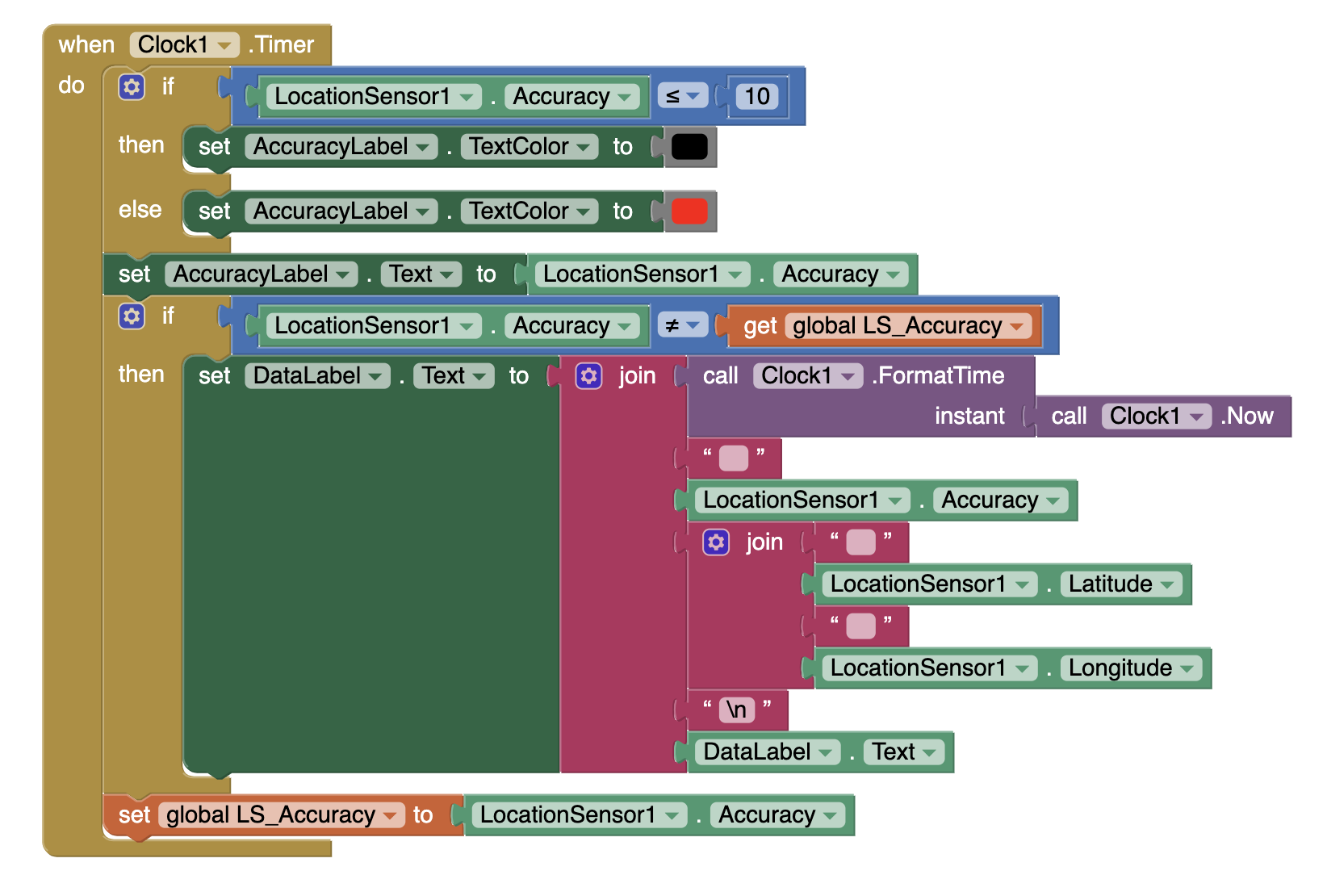
What is the \n in the Text blocks for? This symbol (consisting of a backslash and the character due north) forces a line change in a Label. Placing the symbol in a text cake helps to brand the formatting readable when the DataLabel is updated on the screen.
When does the location sensor 'know' when to bank check for a satellite fix? There are ii backdrop that can trigger this. First is the TimeInterval property. In this app, nosotros've prepare the TimeInterval to 60000, or 1 minute. The LocationSensor volition then cheque each minute for new location information. The DistanceInterval property is another manner to trigger new data. In this app, the property is set to 0, so any location alter detected (after 1 infinitesimal) will trigger the LocationSensor1.LocationChanged event.
Attempt out the app with the MIT AI2 Companion. You should get-go to receive data and the accuracy value should change. If you do not, bank check that your MIT AI Companion app has location permissions turned on in its settings. You should be prompted, but you can also check the app'due south settings.
If y'all build the apk file and install this app on your device, you should also exist prompted during the installation to turn on location permissions for the app. If not, make sure to go into the Settings for the app and turn on location permissions before using the app.
AI2 Location Sensor Examination App
This app is much more circuitous and demonstrates most of the capabilities of the AI2 LocationSensor component. Here is a link to the aia so yous can explore the lawmaking. The ii images below testify a working Location Sensor Exam app. The image to the left shows the sensor exam app in action but prior to touching the Capabilities push. Touch the button and the screen should look like the paradigm on the right. The app confirms the tablet's GPS has all the required capabilities.
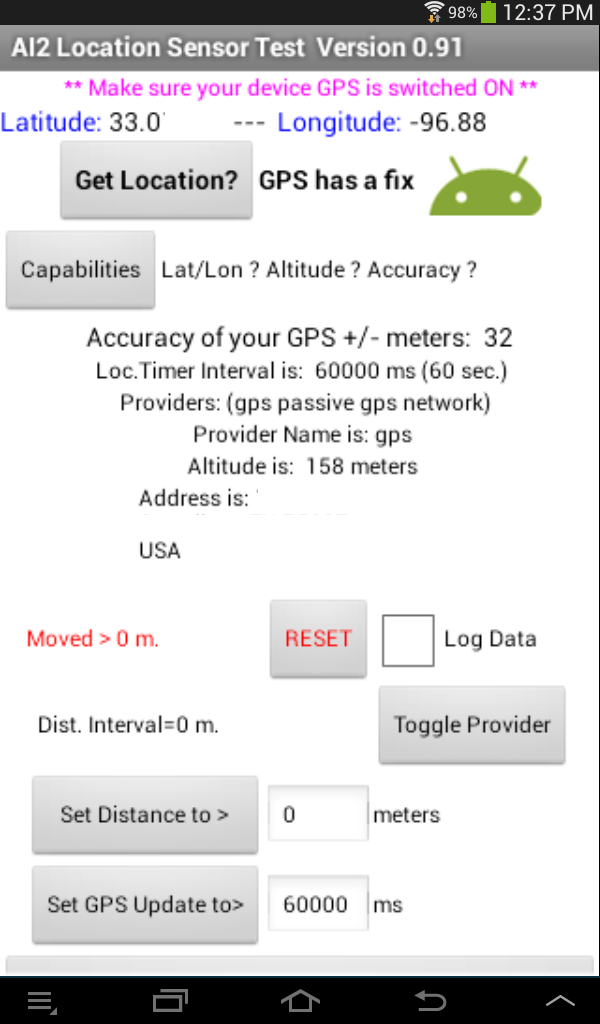
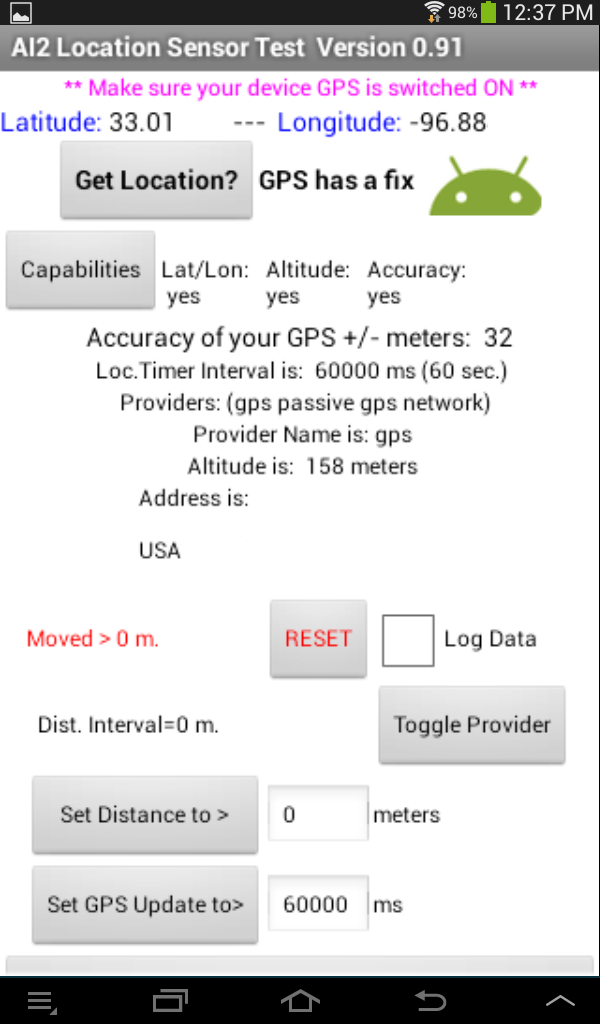
The app features the following:
- Once the "Get Location?" button is pressed, provides Accuracy, Breadth and Longitude information.
- Press the Capabilities button to display whether the Latitude/Longitude, Altitude and Accuracy capabilities exist on the device existence tested. Not all devices accept all these capabilities.
- Reports the Accuracy of each GPS satellite fix in +/- meters. The Accuracy value is the radius in meters around the sensor's detected location. The device has a 68% chance to be located within this radius.
- Displays the available service providers. On a WIFI tablet, you possibly only become 'gps'; on a telephone, at that place will be more options if the phone has a real GPS.
- Displays the currently selected service provider. You lot can change between gps and network past touching the Toggle Provider button. It switches betwixt gps and network within the app simply.
- Reports the Altitude, only only if the device GPS has that adequacy. Practise not look the Distance to alter when you walk from street level to the 3rd floor of a edifice. The measurement is not that accurate.
- Reports the current address, only if a location accost is bachelor.
- Displays if the device has moved more than than the DistanceInterval selected. Read the caveats in the department beneath.
- Allows one to set both the Distance and Time intervals. Altitude is set to 0 as a default; Time to 60000 ms (one minute). Both values are displayed in the app.
- Provides a data log of Accurateness, Latitude, and Longitude over a period of time. Bank check the Log Information box to plough this on.
- Reports whether the GPS has a satellite prepare or non and whether location data is network based. Read about set below.
- Allows resetting the LocationSensor's Fourth dimension and Distance settings to the default past using the "Close the app and reset Location Distance and Time" push.
How a Phone / Tablet "Knows" its Location
Understanding how GPS and Wireless Networks work is necessary to understand the LocationSensor component. Both GPS and Wireless networks provide positional data in different ways. The LocationSensor component can obtain data using either system.
Anything you desire to know most GPS and how GPS receivers works is summarized here: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_Positioning_System. Wikipedia is not always the about authentic source, but in this instance Wikipedia provides a pretty practiced introduction to geolocation concepts.
The GPS satellites broadcast two types of information chosen Almanac and Ephemeris. Annual data includes the satellite orbital parameters. It is precise data and is valid for several months. Ephemeris data includes orbital and clock correction data for each satellite which is necessary for precise positioning. When the GPS is initially turned on, the receiver "looks" for the satellites based on where a satellite is supposed to exist and as described in the Annual and corrected for current time. The GPS determines if the Annual data is valid; if the Almanac is not valid, perchance if the GPS receiver has been turned off for a while, the GPS searches the sky or is internally re-initialized and so information technology can download a new Almanac from a satellite and first over. This is why a fix may take a longer time when a device is first turned on and why subsequent fixes are made more chop-chop.
A GPS receiver needs a clear view of the heaven to get ephemeris / annual data from the satellites. Information technology uses this data to make up one's mind location. Information technology needs measurements from a minimum of iii satellites to provide positional information. GPS receivers generally are capable of using from 12 up to 20 satellites to provide accurate information. Several factors decide how many satellites are used by the GPS in a fix. A limited number of satellites might be visible to the GPS, some satellites could be out of service, or objects may be blocking the satellite and reduce its broadcast indicate strength. In practice, nigh GPSes utilise fewer then 9 or 10 satellites to provide a location fix.
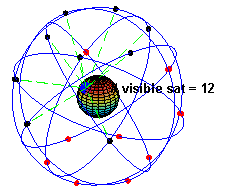
Wireless networks use triangulation to determine the location of a device. The location information is obtained more rapidly than the information obtained from a GPS fix. A GPS fix can have from a few seconds to a minute or so with single channel GPS receivers. A network set is very fast. Nonetheless the data provided by wireless networks is less reliable than near GPS fixes. Mobile phones get the prison cell tower IDs from the nearest three or four prison cell towers in the vicinity. The technology uses the time difference of inflow to get your "exact" location within 10-50 meters of accuracy within 10-15 seconds. This method is called MS-Assistance for GSM phones. A fallback method is chosen Jail cell ID. Cell ID is a passive estimate of nigh i.7 to 8 km (1-five miles) in accurateness and is possibly used if MS-Aid doesn't report sufficient certainty to get a position prepare less than 100 meters (the minimum performance threshold for MS-Aid).
A mobile devices uses a GPS to go an accurate snapshot of the its location while moving or stationary. Wireless networks can be used for stationary positions in the absence of a GPS receiver. The information provided in this tutorial regarding these systems may be out of date as technology improves. Check online for further improvements to GPS and wireless network positioning systems.
What Developers need to know to utilize the LocationSensor Component
To make a successful geolocation based app, the developer has to know how the GPS satellite system works and consider the limitations that exist due to the quality of GPS receivers in mobile devices.
- The LocationSensor component reports latitude and longitude using a period decimal separator.
- The sensitivity of the GPS receivers in unlike devices varies. Some devices are more sensitive to whether the phone/tablet is in a building, under trees or is traveling in canyon similar environments (i.e. in the mountains, between heaven scrapers or merely tall buildings). Buildings obscure the line of sight from the GPS to the positional satellites. Weak signals result in reduced accuracy or loss of fix.
- A GPS receiver'south accuracy is dependent on the number of satellites it can get a fix on (receive and confirm) at whatsoever moment. Consequently, accuracy of location reported by the device can vary easily by plus or minus fifty meters or so over a very curt period of time. GPS accuracy is as well dependent on the quality of the GPS receiver in your device. Existent GPS receivers used for commercial purposes,, non tablets/phones, can exist accurate to inside less than ii meters. Your phone probably has no where near that capability, but it might. Almost GPS have 12 parallel channels. The channels assistance to acquire satellite signals. Some early on GPS receivers had only a single aqueduct, meaning the receiver was slower in acquiring a fix and may not have had the accuracy of a receiver with multiple channels. Newer phones accept receivers that accept 20 channels and A-GPS and GLONASS (GLONASS is the Russian version of GPS) which can operate together. The LocationSensor tin can not handle GLONASS.
- The LocationSensor.DistanceInterval can trigger an unexpected alter of location response when set to a larger number. This tin can occur because the GPS is in a constant state of flux, and sometimes, depending on how may satellite fixes being used, can provide very erroneous location data. An early device trigger response can exist prevented past providing logic blocks to only trigger when the GPS accuracy is within numbers you program.
- When the GPS accurateness is reported by LocationSensor.Accuracy to be 32 meters for case, information technology ways that if a LocationSensor.DistanceInterval is set to anything less than 32 meters, the GPS will attempt a new set up (change) as if the distance is set to 0 meters. The GPS units in low end phones specially are not very precise and some tablets have no GPS at all.
- To empathize how your device's accuracy (positional reliability) changes, use the GPS Accuracy Logger app described above, ready the DistanceInterval to zero, and monitor the changes in accuracy of your GPS.
In review, the GPS receiver in near phones is non precisely accurate. The positional information it provides may be simply +/- 50 meters on average, perhaps equally expert as +/-5 meters on occasion. The Accuracy property tells yous how reliable whatsoever single satellite fix is. The GPS receivers in phones are not very sensitive. The born GPS loses signals in buildings and can be difficult in an urban environment. Not all tablets have a GPS receiver. Those tablets that do non have a GPS receiver accept a much reduced positional accuracy compared to those that have a GPS. Devices without a GPS receiver can utilise triangulation between prison cell telephone towers and/or a wifi location to approximate the telephone's location.
The initial satellite fix on most devices takes almost thirty to 40 seconds to achieve. Subsequent satellite fixes commonly take near 20 seconds on well-nigh devices. When a developer sets the LocationSensor.TimeInterval to 1000ms (one second), the LocationChanged result will trigger but information technology will not update the location in one case a 2nd. A very reasonable TimeInterval might be 20000 ms.
There is an option in the location sensor to make up one's mind proximity to a destination. Experiments indicate this feature is not very authentic when set to small distance changes. Nearly +/- 50 meters reliability might be possible on a regular ground using the LocationSensor.DistanceInterval property. Unremarkably, the GPS 'fires' based on time simply you can besides allow the location sensor to 'burn' based on a altitude moved. I can run across an application mixing the 2 methods. The location will trigger a GPS fix based on time merely it will also attempt to trigger based on move since the last gear up. A ten meter sampling of a location does not seem applied. because a telephone GPS might but be able to resolve +/- fifty meters. See for yourself. Use the LocationSensor1.Accurateness block and sample the accuracy reading every minute and see what y'all get? The GPS Accuracy Logger does this and so the lawmaking is available in this tutorial.
Read the MIT App Inventor's team clarification of the location sensor hither http://appinventor.mit.edu/explore/content/sensors.html.
Downloads
- GPSAccuracyLogger.aia
- LocationSensorTest.aia
0 Response to "Mit App Inventor 2 Get Travel Speed"
Post a Comment